WinToFlash: Ever needed to create a bootable USB drive, but felt overwhelmed by the process? This guide breaks down everything you need to know about WinToFlash, a handy tool for just that. We’ll walk you through creating bootable drives, compare it to other options like Rufus, troubleshoot common problems, and even explore some of its more advanced features.
Get ready to become a bootable USB drive pro!
We’ll cover the basics of WinToFlash functionality, including supported operating systems and a step-by-step guide. Then, we’ll dive into comparisons with alternative tools, addressing security concerns, and exploring advanced options for customization. We’ll also tackle troubleshooting, ensuring you’re prepared for any hiccups along the way. By the end, you’ll be confident in using WinToFlash to create your own bootable USB drives.
WinToFlash Functionality
WinToFlash is a nifty little utility that lets you create bootable USB drives from Windows installation files. Think of it as a bridge between your ISO image and your flash drive, making it super easy to install or repair Windows on a computer without needing a DVD. It simplifies the process, making it accessible even for those less tech-savvy.
Essentially, it bypasses the need for a physical disc and allows for a more streamlined installation process.WinToFlash’s core functionality centers around copying the contents of a Windows installation source (typically an ISO file) onto a USB flash drive, preparing it to boot from the drive. This process modifies the USB drive’s boot sector and file system to correctly load the Windows installation files.
It also handles the necessary partitioning and formatting of the drive to ensure compatibility.
Operating Systems Supported by WinToFlash
WinToFlash primarily supports various versions of Microsoft Windows. While the exact versions supported might vary slightly depending on the specific version of WinToFlash used, it generally handles Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8, 8.1, and 10 installation media. Support for Windows 11 is less consistent across different versions of WinToFlash, so checking compatibility before use is recommended. It’s crucial to ensure your WinToFlash version aligns with the target Windows OS for successful bootable USB creation.
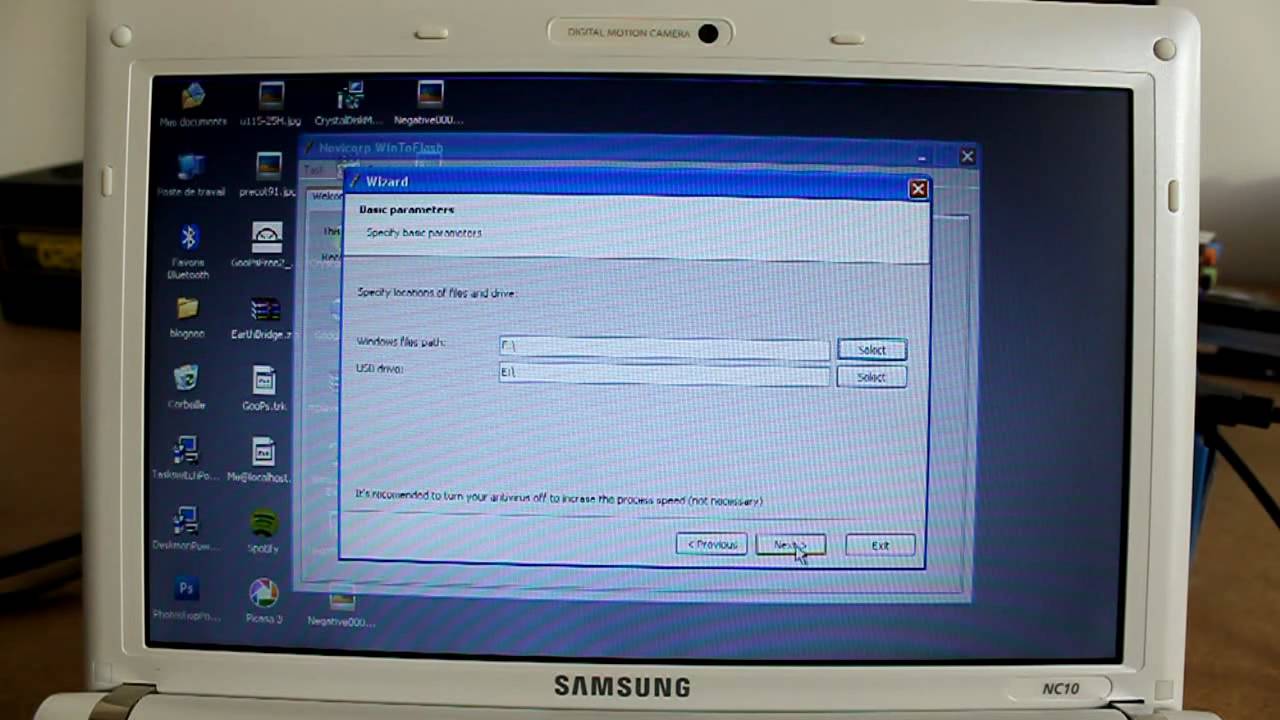
Creating a Bootable USB Drive with WinToFlash: A Step-by-Step Guide
First, you’ll need a few things: a USB flash drive (at least 4GB, but larger is recommended), a Windows installation ISO file, and the WinToFlash application itself. Remember to back up any data on the USB drive, as the process will erase everything on it.
- Download and Install WinToFlash: Download the WinToFlash executable from a trusted source and install it on your computer.
- Run WinToFlash: Launch the WinToFlash application.
- Select the Installation Source: Browse and select the path to your Windows installation ISO file.
- Select the USB Drive: Choose the USB flash drive from the list of available drives. Be absolutely certain you select the correct drive; selecting the wrong one could lead to data loss.
- Choose Options (if applicable): Some versions of WinToFlash offer additional options, such as formatting the drive with a specific file system. Review these carefully before proceeding.
- Start the Process: Click the button to begin creating the bootable USB drive. This process will take some time, depending on the size of the ISO file and the speed of your computer.
- Verification: Once the process is complete, verify the bootable USB drive by attempting to boot from it on a computer.
Flowchart for Creating a Bootable USB Drive with WinToFlash
The process can be visualized using a simple flowchart:[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would start with a “Start” oval. Then a rectangle “Download and Install WinToFlash”. Next, a rectangle “Run WinToFlash”. Then a diamond “Select ISO and USB Drive”.
From the diamond, a “Yes” arrow goes to a rectangle “Choose Options (if any)”. From the “Choose Options” rectangle, an arrow goes to a rectangle “Start Creation”. From the “Start Creation” rectangle, an arrow goes to a rectangle “Verify Bootable Drive”. From the “Verify Bootable Drive” rectangle, an arrow goes to an “End” oval. The “No” arrow from the diamond goes back to the “Select ISO and USB Drive” diamond, indicating a need to re-select the source and destination.]
WinToFlash Alternatives
Okay, so you’re looking at WinToFlash, but maybe you’re wondering if there are better options out there. Let’s dive into some alternatives and see how they stack up. We’ll compare features, ease of use, and overall effectiveness.
WinToFlash vs. Rufus: A Feature Comparison
WinToFlash and Rufus are both popular tools for creating bootable USB drives, but they have some key differences. Rufus, for instance, boasts a simpler interface, making it incredibly user-friendly, even for beginners. It’s also known for its speed and efficiency in creating bootable media. WinToFlash, on the other hand, offers more advanced options and supports a wider range of ISO images and operating systems.
However, this added functionality can sometimes make it feel a bit more complex to navigate. Ultimately, the “better” tool depends on your technical skill level and specific needs. If you need a quick and easy solution, Rufus is probably the winner. If you need more control and flexibility, WinToFlash might be a better fit.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using WinToFlash and Similar Tools
Using tools like WinToFlash offers several advantages. They streamline the process of creating bootable USB drives, eliminating the need for complex command-line operations. This simplifies tasks like installing operating systems or running diagnostic tools. However, using these tools also comes with some drawbacks. Some tools might lack support for certain operating systems or ISO images, limiting their versatility.
Additionally, relying on third-party tools introduces a degree of risk, as there’s always a potential for malware or other security issues if you download from untrusted sources. Always download from the official website of the software you intend to use.
Three Alternative Tools to WinToFlash
Here are three strong contenders to WinToFlash: Rufus, UNetbootin, and BalenaEtcher.
Comparison of Alternative Tools
| Tool | Key Features | OS Compatibility | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rufus | Simple interface, fast creation, supports various ISO images, GPT partitioning | Windows | Very Easy |
| UNetbootin | Supports various operating systems (including Linux distributions), can create bootable drives from ISO images or downloaded distributions | Windows, macOS, Linux | Easy |
| BalenaEtcher | Open-source, cross-platform, focuses on security and image verification, supports various image formats | Windows, macOS, Linux | Easy to Moderate |
Troubleshooting WinToFlash Issues
WinToFlash, while generally straightforward, can sometimes throw curveballs. Understanding common problems and their solutions can save you significant frustration and time. This section provides a troubleshooting guide to help you navigate those bumpy patches and successfully create your bootable USB drive. We’ll cover common errors, formatting problems, boot failures, and how to ensure your ISO image is squeaky clean before you even start.
Common Errors and Solutions
Many WinToFlash errors stem from simple oversights or compatibility issues. For instance, using a USB drive that’s too small for the Windows installation files is a frequent culprit. Another common issue is selecting the wrong ISO file or having a corrupted ISO. Insufficient permissions can also block the process. Below is a table outlining some common errors and their solutions.
| Error Message (or Symptom) | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| “Insufficient Disk Space” | The USB drive doesn’t have enough free space. | Use a larger USB drive or delete unnecessary files from the drive before starting. |
| WinToFlash crashes or freezes. | Corrupted ISO file, insufficient system resources, or driver conflicts. | Try a different ISO, close unnecessary programs, and update your drivers. Consider running WinToFlash as administrator. |
| USB drive not recognized. | Faulty USB drive, driver issues, or incorrect USB port. | Try a different USB port, a different USB drive, and update your USB drivers. Check Device Manager for errors. |
| “Access Denied” | Insufficient permissions. | Run WinToFlash as administrator. |
| Boot failure after installation. | Incorrect ISO, corrupted installation files, or BIOS settings. | Verify the integrity of your ISO, try a different ISO, and check your BIOS settings (especially boot order). |
Resolving USB Drive Formatting and Boot Failures
Formatting issues often arise from incompatible file systems or errors during the formatting process. Boot failures, on the other hand, can be due to incorrect BIOS settings or problems with the created bootable drive. Let’s address these separately.
USB Drive Formatting Problems
Before using a USB drive with WinToFlash, ensure it’s properly formatted. The recommended file system is usually FAT32 for broader compatibility, though some newer Windows versions might require NTFS. Using the wrong file system can lead to boot failures. If you encounter formatting errors, try using a different formatting tool, like the built-in Windows Disk Management utility, ensuring you back up any important data first.
A faulty USB drive might also be the cause; test with a different drive if possible.
Boot Failure Resolution
If your computer doesn’t boot from the USB drive, the first thing to check is the BIOS settings. Ensure the USB drive is listed as the primary boot device in the boot order. Also, make sure the USB drive is properly connected and recognized by the BIOS. If the problem persists, verify the integrity of the ISO image used to create the bootable drive (as discussed below).
Verifying ISO Image Integrity
Using a corrupted ISO image is a recipe for disaster. Before using WinToFlash, it’s crucial to verify the integrity of your ISO file. You can do this by calculating the checksum of the downloaded ISO file and comparing it to the checksum provided by the source. Many ISO sources provide MD5 or SHA-1 checksums. You can use a checksum utility (easily found online) to calculate the checksum of your downloaded file.
If the calculated checksum matches the provided checksum, you can be reasonably confident that the ISO is intact and hasn’t been corrupted during download. A mismatch indicates a problem, requiring you to redownload the ISO. This seemingly small step can prevent hours of troubleshooting later.
Security Aspects of WinToFlash
Creating bootable USB drives with WinToFlash offers convenience, but it also introduces potential security vulnerabilities. Understanding these risks and implementing best practices is crucial to protect your data and system. Failing to do so could expose your system to malware or unauthorized access.Using WinToFlash, like any software involving system-level modifications, carries inherent security risks. Improper usage can lead to data loss, system instability, or even compromise your computer’s security.
The process of creating a bootable drive involves writing data to a storage device, which, if mishandled, can result in unintended consequences. This is why understanding and implementing security best practices is paramount.
Potential Security Risks Associated with Using WinToFlash
The primary security risks associated with WinToFlash stem from the use of untrusted ISO images and improper handling of the bootable USB drive. Downloading a malicious ISO image and creating a bootable drive from it could lead to the installation of malware on your system, potentially compromising your data and privacy. Additionally, leaving the bootable USB drive unsecured could allow unauthorized access to its contents, including sensitive information.
Physical security of the drive is just as important as the digital security of the image it contains.
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Security When Using WinToFlash
Safeguarding your data requires a multi-faceted approach. First, always download ISO images from trusted sources, such as official software vendor websites. Verify the integrity of downloaded files using checksums (MD5 or SHA-256) to ensure they haven’t been tampered with. Second, use strong passwords to protect your computer and any accounts that may be accessed from the bootable drive.
Third, after creating the bootable USB drive, consider encrypting it using tools like BitLocker (Windows) or VeraCrypt to protect the data on the drive from unauthorized access, even if the drive is lost or stolen. Finally, always physically secure the USB drive when not in use.
Importance of Using Trusted ISO Images and Verifying Their Authenticity
Using a trustworthy ISO image is the cornerstone of secure WinToFlash usage. Downloading from untrusted sources exposes your system to malware risks. Verifying authenticity through checksum comparison ensures the downloaded file matches the expected integrity. This comparison involves generating a checksum of the downloaded file and comparing it to the checksum provided by the legitimate source. A mismatch indicates potential tampering or corruption.
For example, if you download a Windows 10 ISO, Microsoft provides the checksum; you should generate your own checksum and compare them for verification.
Securing the Bootable USB Drive Created with WinToFlash
Once the bootable USB drive is created, physical and digital security measures should be implemented. Physically, store the drive in a safe place to prevent unauthorized access. Digitally, consider encrypting the drive using appropriate software to prevent data access even if the drive is lost or stolen. Regularly scan the drive for malware using a reputable antivirus program.
And, of course, remember to safely eject the drive from your computer before disconnecting it to prevent data corruption.
Advanced WinToFlash Features
WinToFlash, while seemingly straightforward, packs some powerful features under the hood that can significantly enhance your bootable USB creation experience. These advanced options allow for fine-grained control over the process, enabling you to optimize performance and tailor the drive to specific needs. Understanding and utilizing these features can make the difference between a sluggish, unreliable boot drive and a fast, efficient one.
Many users only scratch the surface of WinToFlash’s capabilities, sticking to the default settings. However, delving into the advanced options unlocks a world of customization, allowing for everything from optimizing boot speed to integrating additional drivers for specialized hardware. This section will explore these advanced features and illustrate their impact on the final bootable USB drive.
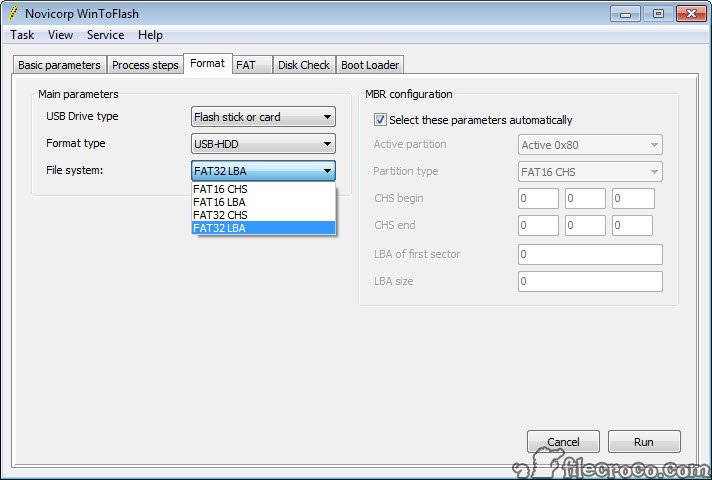
Partition Scheme and File System Selection
The choice of partition scheme (MBR or GPT) and file system (FAT32, NTFS, exFAT) significantly affects compatibility and performance. MBR is generally compatible with older BIOS systems, while GPT offers larger partition sizes and improved data integrity, ideal for modern UEFI systems. Similarly, the file system choice impacts compatibility with different operating systems and the maximum file size supported.
Selecting NTFS offers better security and larger file support but might not be universally compatible with all systems, while FAT32 is widely compatible but limits file sizes. Choosing the correct options ensures your bootable drive works flawlessly across different hardware and software environments.
Bootloader Configuration
WinToFlash allows you to configure the bootloader, the crucial piece of software that initiates the boot process. Advanced settings might include selecting specific bootloader versions, tweaking boot parameters, or integrating additional boot entries. For instance, you could configure the bootloader to prioritize a specific driver or enable debugging options. Proper bootloader configuration is vital for ensuring a smooth and reliable boot process, preventing common issues like boot failures or system instability.
Driver Integration
Some advanced versions of WinToFlash allow for the integration of additional drivers onto the bootable USB drive. This is particularly useful when installing an operating system on a system with specialized hardware (e.g., RAID controllers, network cards). By including the necessary drivers, you avoid potential installation roadblocks caused by missing hardware support. This step requires identifying and correctly integrating the necessary drivers; incorrect driver integration can lead to system instability or failure to boot.
Advanced Options Summary
The following table summarizes the effects of various advanced options on the bootable drive creation process. Careful consideration of these options is crucial for creating a reliable and efficient bootable USB drive.
| Option | Effect |
|---|---|
| Partition Scheme (MBR/GPT) | Determines compatibility with BIOS/UEFI systems and maximum partition size. |
| File System (FAT32/NTFS/exFAT) | Impacts compatibility with different operating systems and maximum file size. |
| Bootloader Configuration | Affects boot speed, stability, and the ability to load specific drivers or debug options. |
| Driver Integration | Adds support for specific hardware components, potentially resolving installation issues. |
| Pre-boot Environment Customization (if available) | Allows for the inclusion of specific tools or utilities in the pre-boot environment. |
System Requirements for WinToFlash
WinToFlash, while generally a lightweight utility, still requires a minimum level of system resources to function correctly. Understanding these requirements ensures a smooth and trouble-free experience when creating bootable USB drives. Failing to meet these minimums could lead to errors, crashes, or an inability to complete the process. This section details the necessary specifications to run WinToFlash effectively.
Operating System Compatibility
WinToFlash supports a range of operating systems, ensuring broad accessibility. However, compatibility might vary slightly depending on the specific version of WinToFlash being used. Always check the software’s documentation for the most up-to-date compatibility information. Generally, it’s compatible with various versions of Windows, ranging from older versions like Windows XP to the latest releases. Support for other operating systems like macOS or Linux is typically not provided.
Hardware Requirements
Sufficient system resources are crucial for optimal WinToFlash performance. While the minimum requirements are relatively modest, exceeding them will result in a faster and more stable process. Insufficient RAM, for instance, can lead to slowdowns or even crashes during the bootable USB creation process. A faster processor will also speed up the overall time taken to create the bootable media.
Minimum and Recommended System Requirements
The following table summarizes the minimum and recommended system requirements for running WinToFlash. These specifications are general guidelines, and actual performance may vary based on individual system configurations and the size of the ISO image being used. Remember that using a USB drive that meets or exceeds the recommended specifications will lead to a smoother and more reliable experience.
| Specification | Minimum | Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| Operating System | Windows XP SP3 or later | Windows 10 or 11 |
| Processor | 1 GHz | 2 GHz or faster |
| RAM | 512 MB | 1 GB or more |
| Hard Drive Space | Sufficient space for the ISO image | Sufficient space for the ISO image and temporary files |
Legal and Licensing Information for WinToFlash
WinToFlash, like many software utilities, operates under a specific license that dictates its usage rights. Understanding these terms is crucial for both users and developers to avoid legal issues. This section will clarify the licensing model, explore the legal implications of various uses, and identify the team behind this handy tool.The licensing terms for WinToFlash are not explicitly stated on a readily accessible central website or within the software itself.
This lack of readily available information makes it difficult to definitively state the exact license. However, based on common practices for similar open-source or freeware utilities, it’s likely governed by a permissive license, such as the GNU General Public License (GPL) or a similar framework that allows for free use, modification, and distribution, potentially with certain conditions. It is strongly recommended to examine any accompanying documentation or contact the developers directly for explicit confirmation of the licensing terms.
WinToFlash Licensing Model
Determining the precise licensing model for WinToFlash requires further investigation. Many free utilities operate under a permissive open-source license or a proprietary license that grants free use but restricts modification or redistribution. Without official documentation, we cannot definitively state the license type. However, users should proceed with caution and assume that, unless otherwise specified, redistribution for commercial purposes or modification and re-distribution might be restricted.
Legal Implications of WinToFlash Usage
The legal implications of using WinToFlash depend heavily on its intended purpose. Using it for personal, non-commercial purposes to create bootable USB drives for personal use or system repair is generally considered acceptable under most licensing agreements, assuming the license permits free use. However, using WinToFlash for mass production of bootable drives for resale or commercial distribution without proper licensing would constitute a copyright violation and could result in legal repercussions.
Similarly, modifying the software’s code and redistributing it without permission would also likely violate the license terms.
WinToFlash Developers and Maintainers
Pinpointing the exact developers or maintainers of WinToFlash presents a challenge due to the lack of readily available information. Many freeware and open-source projects lack centralized, easily accessible information about their development team. To identify the responsible parties, one might need to delve into the software’s source code (if available), examine older forum discussions, or contact individuals who have contributed to the project’s development and maintenance.
Accessing Official Licensing Documentation
Unfortunately, readily available and easily accessible official documentation regarding WinToFlash licensing and usage rights is currently lacking. The absence of a dedicated website or clearly stated licensing information makes confirming usage rights difficult. This highlights the importance of exercising caution and assuming responsible use until more detailed licensing information is made publicly available.
WinToFlash and Different ISO Images

WinToFlash, while primarily known for its Windows image handling, is surprisingly versatile when it comes to creating bootable USB drives from various ISO images. The process is largely similar regardless of the operating system, but certain nuances and potential compatibility issues exist depending on the specific ISO. Understanding these differences can save you time and frustration.The core process involves selecting the ISO image, choosing the USB drive, and initiating the creation process within WinToFlash.
However, factors like the ISO’s file system (e.g., FAT32, NTFS, ext4), boot loader type, and the architecture (32-bit or 64-bit) can influence compatibility and the success of the operation. Linux distributions, for example, often require specific partition schemes and boot loaders that might differ from those expected by Windows-centric tools.
ISO Image Compatibility
WinToFlash generally supports a wide range of ISO images, including various Windows versions (Windows 7, 8, 10, 11, Server versions), numerous Linux distributions (Ubuntu, Fedora, Mint, Kali, etc.), and even some other specialized operating systems. However, certain less common or older ISO images might present compatibility problems. Issues can stem from outdated boot loaders, unusual partition structures, or the presence of drivers incompatible with WinToFlash’s internal mechanisms.
Successfully creating a bootable drive depends on the ISO image being properly formatted and structured for the target system architecture.
Handling Incompatible ISO Images
When encountering an incompatible ISO image, WinToFlash may display error messages indicating the problem. These messages can range from general incompatibility errors to more specific issues like incorrect boot sector information or file system errors. The first step in troubleshooting is carefully reviewing the error message to pinpoint the source of the problem. If the issue is related to the file system, attempting to convert the ISO image to a different file system (using a tool outside of WinToFlash) might resolve the issue.
If the error points to the boot loader, you might need to use a different tool specifically designed for the particular ISO image’s boot loader type. In some cases, the ISO itself might be corrupted, requiring you to download a fresh copy.
Commonly Used ISO Images and WinToFlash Compatibility
The following table summarizes the compatibility of commonly used ISO images with WinToFlash. Note that compatibility can depend on the specific version of the ISO and WinToFlash. It is always advisable to consult the documentation for both the ISO and WinToFlash for the most up-to-date information.
| ISO Image | WinToFlash Compatibility | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 10/11 | Generally Excellent | Direct support, often requiring minimal configuration. |
| Ubuntu | Generally Good | May require specific settings depending on the Ubuntu version. |
| Fedora | Generally Good | Similar to Ubuntu, version-specific considerations might be necessary. |
| Older Windows Versions (XP, Vista) | Potentially Problematic | May require additional drivers or adjustments. |
| Custom Linux Distributions | Variable | Compatibility highly dependent on the distribution’s build and boot loader. |
Future Developments and Improvements for WinToFlash

WinToFlash, while a solid tool, has room for growth and improvement. Future development should focus on enhancing usability, expanding compatibility, and integrating with evolving operating system technologies. By addressing user feedback and anticipating future trends, WinToFlash can solidify its position as a leading utility for creating bootable USB drives.Future updates could significantly improve the user experience and broaden the application’s capabilities.
A focus on modern design principles and intuitive workflows will enhance its appeal to a wider audience.
Enhanced User Interface and User Experience
The current WinToFlash interface, while functional, could benefit from a modern redesign. Imagine a cleaner layout with improved visual hierarchy, using clearer icons and more intuitive navigation. For example, a streamlined wizard-style interface could guide users through the process step-by-step, reducing confusion and errors. The addition of progress bars and clearer feedback messages would also greatly improve the user experience, providing reassurance and transparency during the often lengthy process of creating a bootable drive.
So, you’re messing around with WinToFlash, right? Creating bootable USBs can be a lifesaver, especially if you’re working on a project that requires specific software. For example, if you’re into design, you might need to install some serious cad software onto a virtual machine. Getting that all set up on a portable drive using WinToFlash is a total game changer for portability and efficiency.
Then you can easily boot up your CAD projects anywhere.
Error messages could be improved to be more specific and offer actionable troubleshooting advice.
Improved Compatibility and Support for New Technologies
Future versions of WinToFlash should proactively address compatibility issues with emerging operating systems and hardware. This includes supporting the latest UEFI firmware standards and ensuring seamless integration with newer USB drive formats and technologies. For example, incorporating support for the latest versions of Windows and potentially expanding to support other operating systems like Linux distributions would significantly broaden the tool’s appeal.
Adding support for different ISO image formats beyond the currently supported ones would also enhance its versatility.
Integration with Cloud Services
Integrating WinToFlash with cloud storage services like OneDrive, Google Drive, or Dropbox could streamline the workflow for users who store their ISO images online. This would allow users to select and use ISO files directly from their cloud storage, eliminating the need for manual downloads and potentially speeding up the overall process. This feature would mirror the convenience offered by similar tools that integrate with cloud storage for other tasks.
Advanced Features and Automation
Adding features such as automated drive formatting and partition creation would simplify the process for less tech-savvy users. Options for creating multiple bootable drives simultaneously or scheduling tasks could enhance productivity for advanced users. Implementing a feature to verify the integrity of the created bootable drive after creation, ensuring a successful boot, would add a significant layer of assurance.
This would be similar to the verification processes used in other disk imaging tools.
Adaptive System Requirements
WinToFlash could adapt to changes in operating system technologies by incorporating automatic system checks and providing tailored recommendations for optimal performance based on the user’s system configuration. This would ensure the tool remains functional and efficient across a wide range of hardware and software configurations. For example, the software could detect the user’s system architecture (32-bit or 64-bit) and automatically select the appropriate drivers and settings, minimizing potential compatibility problems.
Outcome Summary
Creating bootable USB drives doesn’t have to be a tech-head’s nightmare. WinToFlash simplifies the process, offering a user-friendly interface and a range of features. This guide has covered the essential aspects of using WinToFlash, from basic functionality to advanced options and troubleshooting. Remember to always prioritize security by using trusted ISO images and following best practices. So go forth, create those bootable drives, and conquer your next tech challenge!
Query Resolution
Is WinToFlash free to use?
That depends on the specific version. Check the licensing information for the version you’re using.
What if my USB drive isn’t showing up in WinToFlash?
Try restarting your computer, checking the USB port, and ensuring the drive isn’t faulty. If it’s still not detected, try a different USB port or cable.
Can I use WinToFlash to create a bootable drive from a downloaded Windows ISO?
Yes, WinToFlash supports various Windows ISO images. Make sure you download the ISO from a trusted source like Microsoft.
My bootable drive isn’t booting! What should I do?
Check your BIOS settings to ensure the boot order prioritizes the USB drive. Also, verify the integrity of the ISO image you used.
Are there any size limitations for the USB drive I can use with WinToFlash?
While WinToFlash doesn’t have a strict size limit, using a larger drive is generally recommended, especially for larger operating systems.